Hello, welcome to the official website of Yunnan Shangri-La Balagezong Tourism Development Co., Ltd!

02
2015
-
12
Origin and Formation of Tibetan Medicine
作者:
Tibetans are one of the ethnic groups with a long history and glorious culture in China. Tibetan medicine is the five outstanding inventions of the Tibetan people (the five small inventions and the five great inventions are ten Ming. The five Ming: rhetoric, rhetoric, rhyme, drama, astrology; the five Ming: technology, medicine, phonology, orthotics, Buddhism.) One of the great culture. It is a summary of the experience of our ancestors in the struggle against various diseases on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau since ancient times. In the long historical development, we have absorbed many essences of other fraternal nationalities and foreign medicine, and constantly supplemented, improved, invented and created it. It has become a scientific and complete theoretical system with revolutionary national characteristics. It is not only for the Tibetan people, but also for the survival of other fraternal nationalities, it has also made a huge contribution.

Tibetan medicine is an ancient science with a long history of more than 2300 years. If it is traced back to the prehistoric legend, it will be even longer. This discipline is a bright pearl in the treasure house of Chinese medicine. It is the experience of Tibetan ancestors in fighting against diseases in their long production and life practice. It draws lessons from and absorbs the essence of medicine from fraternal nationalities and neighboring countries, and combines the development and utilization of Tibet's conditions and drug resources. Through continuous description and repeated practice, it has gradually improved, the formation of a body of human physiology, pathology, diagnosis, treatment, prescriptions, preparations and special treatment and other aspects of the system, complete and ultimately formed a distinctive national medical system. The details of these aspects have been recorded in the early history books, religious origins and medical history, and are only briefly introduced.
According to the history of Xiangxiong Bon religion, it was at least 2,000 years ago in a credible historical material. According to the textual research, the Bon Patriarch Xin Rao Mivozi lived in the same period as Buddha Sakyamuni. Some other historical materials believe that around 400 to 500 BC, it was the formative period of Bon medicine. At this time, Chang Songjie Puchi carried forward many medical classics written by his father Xin Rao Mivozi. There are also some historical records of the origin of Bon religion that the ancestor of Bon religion, Xin Rao Mivozi, came to the world and founded medicine. Although there are different opinions, one thing is certain, that is, Tibetan medicine has a very long history. From the perspective of the history of Nechizam and Pechsi, it is now recognized that Tibetan medicine has a history of more than 2300 years, which is based on the above-mentioned point of view.
In addition, according to the "Five Proverbs-Minister's Proverbs", when Nie Chizanpu came to the place of Yalongzantang, Zilaga jumped to answer one of the six doubtful points, saying that there is medicine if it is poisonous. So how to make poison into medicine in the early stage? According to the research, there was a kind of pill called "spit boom day" which was taken from the internal organs of animals at that time. Its record was found in the Poison Therapy written by Jepchissi edited by Tibetan medicine scientist Tima Geshidan Zengpingcuo, which is obvious to all till now. According to the historical chapters of the Encyclopedia of Chinese Medicine, the sub-volume of Tibetan Medicine, edited by the famous Tibetan medical scientists Qiang Ba Chilie and Tudeng Tsering, the ancestor of the world, King Brahma, taught people to cure dyspepsia with boiled water with his compassion for mankind. It is inferred that the first human disease is dyspepsia. Because people in primitive society ate pure rough food, resulting in a lot of dyspepsia, later people found a way to use fire, against raw, cold, indigestible food, through the method of burning or boiling, not only to prevent dyspepsia, but also through practice has proved that boiled water to increase body heat, help digestion, but also for the auxiliary treatment of other diseases is also beneficial, due to the development of agricultural and animal husbandry production, people not only invented the method of mixing milk to extract ghee, learned to treat trauma, used "ghee to stop bleeding, distiller's grains to treat sores" and other methods, but also found some new sources of drugs.

The 28th generation of Tubo Dynasty Zanplatutozan (AD 254-374, the Tibetan king married his princess Yiji Ruicha to Tianzhu's medical scientist Biqi Gaqi as his wife. Later, they gave birth to a son named Tonggatujue, his parents and another Tianzhu medical scientist, Bigarazi, taught him "Shengjing", "Food Sutra", "Medicine Sutra", "Bloodletting Fire Sutra", "Medical Equipment and Artificiously Sutra" and so on without reservation, making him proficient in everything and becoming a famous doctor. In the hand-copied sutra "Medical Sunlight", it is explained that medicine has been greatly developed during the period of Ratto's Nian Zan, and has begun to understand the principle of the nature of cold and heat in medicine. This is very consistent with the view that there is a difference between cold and heat in the postscript of the Four Medical Codex. There was also a Tubo king named Mo Longbao Bazaar, who was born blind and was cured by a golden knife through Tuyu Hunyan. When he first opened his eyes, he saw the argali sheep on Mount Damo, so he changed his name to Darinian. Tubo Wang Zhongnian Dewu, suffering from dragon leprosy, the Lord to avoid genetic offspring, their own born into the cave, this story is recorded in the frescoes of Sangye Temple. There is also a tomb "Sunchedongbu" built in Yalon Xiangda (Xiangduo), but it was a pity that this tomb was wiped out during the civilian uprising. The above facts are sufficient to explain the development of Tibetan medicine during the period of Ratto's Nian Zan. At that time, doctors like Tong Ge Tuojian appeared, who were able to open the eyes of Morong Baobazar. The fact that Zhong Nian De Wusheng entered the cave indicates that the doctors, medical treatment and prevention techniques of that era reached a very high level. Dr. Tonggatujue served as the chief physician for the second half of his life and the first half of his life. From then on, Tongge Tuojue's imperial doctor, five generations of father and son, served as the imperial doctor of the 29th to 33rd generation of Tibetan kings. About (7th century AD) when the Tibetan king Nang Ri Songzan, he absorbed some knowledge of medicine and astronomy from the Han Dynasty. Although it has not been greatly developed, it shows that since then, he has found a way to absorb the advantages of other medicine and make the national medicine develop.
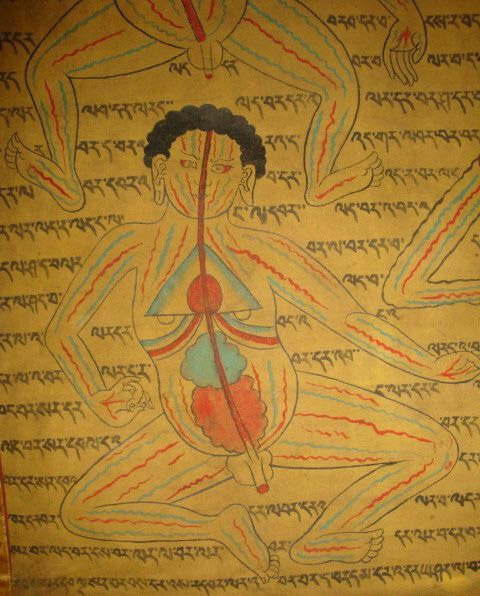
Yutuingma Yundan Gongbu (now commonly known as Lao Yutuo), born in 708 AD, is a great Tibetan medicine scientist. He lived to be 125 years old. He used the results of previous research to train doctors and practice medicine. disease. At the same time, it has absorbed the rich medical essence of ancient India, Nepal, Kashmir, Chong (now Xinjiang) and other places, as well as the wonderful efficacy of traditional Chinese medicine in the motherland. In particular, on the basis of Bai Ruochana's works such as "four successive interpretation of difficult light", he wrote the masterpiece "four medical classics" of Tibetan medicine in his lifetime. He has also written "Four Continued Interpretation of Difficulties", "Eighteen Medical Continuation", ("The Essentials of Famous Doctors in Hanji, Tianzhu, Nepal and other places") and "Yutuo Fangli Opinions" and other works. "Four Medical Classics" is commonly known in Chinese, the full name is "Ganlu Qingyi Eight Secret Formula Continuation", and the Tibetan translation is "Suori Jusi". This is a book with both Tibetan local characteristics and Chinese medicine and Tianzhu medicine. The appearance of the comprehensive masterpiece of Tibetan medicine has promoted the development of Tibetan medicine and expanded its scope of influence. This is not only the difference in the content and characteristics of the "Four Medical Classics", but also the glorious culture of the nation. Therefore, it has been praised and admired by experts and scholars at home and abroad, and has become a priceless treasure in the field of scientific research. Master Yu Tuoningma has been to many areas of Handi, Tibet, India and Nepal for many times, developing medical activities and teaching medical theories on a large scale, going to Nyingchi Medicine City in Tibet, establishing medical monasteries, teaching medical theories based on the "Four Medical Classics", training more than 1,000 disciples, and compiling many classics on medicine and astronomy for future generations. Later generations called it "the second medicine king".
Around 1000 A. D., when Guge Wang Ke was in power during the period of Yexiwei, Banzhi Dharma Room Woma and Niewo translator Youge Renqing jointly translated the first medical classics after the collapse of the Tubo Dynasty, "Eight Medical Collections to Be Self-released". This translation is a new milestone in the vigorous development of Tibetan medicine.
From 950 to 1005 A. D., great translator Ren Chin Sangbu translated "Eight Collection Points" and its notes by Ma Ming on Master and "Moonlight with Wide Note on Word Meaning" by Cagamero scholar Dawanga. Renqin Sangbu is not only a famous translator of medical classics, but also a scholar who is proficient in medicine. His translations have a profound impact on the development of Tibetan medicine.
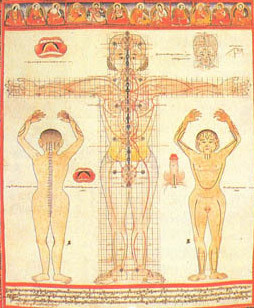
In the 10th century AD, Yutusama Yundan Gongbu (now commonly known as "Xin Yutuo") was the 13th generation descendant of Yutuimingma and was born in Guoxi Retang, Gyangzi County, Tibet. According to the postscript "Follow-up Blue Glaze" written by Disi Sangjegyatso, Utosama and Zhongguoba Jevajiong are figures of the same period. After the 10th century, with the permission of the fifth Dalai Lama, his biography was inscribed in the woodblock of the Gadan Bucuolin Temple. Utosama has traveled through Nepal and Sri Lanka six times with various strange magical powers. In the first half of his life, he mainly studied and taught eight branches of medicine. Later, he took Wei Badaza and Raodun Gongqujia as his teachers, and after learning all the contents of the "Four Medical Classics", he temporarily studied in a solo way. When I went to India several times, I personally met with many great scholars and great achievers, such as the master of the mother of the air, the mother of the air, and the immortals of the Zaryga, and got numerous wonderful tips. In his own book, he said: "The eight branches of holy language medicine, the dragon tree medicine, the black and white moonlight, the immortal's pakkui medicine, the Han Indian saints medicine, the Tibetan practice experience, and the empty mother teaching, etc., rely on the disciple's blessing to learn from the teacher, practice in the past, self-body and mind, and wisdom in this world". As mentioned above, on the basis of a comparative study of all the medical classics circulating in the snow region at that time, Yuto Sama first compiled a five-part medical book, "Visiting Pulse Diagnosis. Since then, a letter of "Clinical Pamphlet" has been compiled, and the manuscript is now in the library of the Tibetan hospital. Later, he wrote the book "The Essence of Small Continuation of Gan Lu", with 33 chapters. In order to understand its secret, he wrote the book "The Golden Spoon of Teaching Commandments" with three scrolls and six articles. At the same time, he also compiled the Great Materia Medica, which contains 199 kinds of medicinal materials, and many other works, such as the secret essence, Bengu Promotion, the Pulse-taking Guidelines, the Secret Treasure Bottle, the Body Cavity and Meridian Chart, in particular, according to the needs of the time, Yutosama Yundan Gongbu supplemented some chapters of the Fundamental Medical Code and the chapters of tea drinking, medicine and food in the Lun Shuo Medical Code. At the same time, according to the contents of "Yuemang Medicine Diagnosis" in the department pulse examination of urine and the relationship between the five elements of mutual birth, chemical, gram and nourishing, etc., the "Follow-up Medical Code" and "Secret Medical Code" are supplemented accordingly. In particular, the essence of the eight medical content is summarized and edited. The saint's disciples are as numerous as the stars in the sky. The most famous of these is Thornton Ixizon. Utoussa taught the Four Gist to this disciple. Sondon compiled "Yutuo Biography · Five-body Self-made" and "Secret Biography", "On the Interpretation of Medical Classics · Small Collection of Light" and other works, and at the same time vigorously promoted the content of "Four Medical Classics. After Yutusama first taught the "Four Medical Classics", in order to let the proud students and disciples understand its meaning, he wrote two medical books, annotated "Color Sign" and "Song Sign" respectively, and wrote "Thirteen Branches" and other works to teach the "Four Medical Classics", which made Tibetan medicine flourish.
最新动态
2022-08-23
The current outbreak, the responsibility is on the shoulder, Balagzon in action!
Since the outbreak of the epidemic in Tibet on August 7, 2022, a large number of tourists from Tibet to Yunnan have entered Shangri-La from National Highway 214. The People's Government of Diqing Prefecture has issued a series of relevant policies and measures and actively responded. Medical staff, police and other front-line personnel stick to the front line, have been involved in the "war of resistance" of the epidemic without gunpowder smoke, and jointly participate in dealing with a major public health security incident faced by mankind.



